 Hydrocele:
Hydrocele:
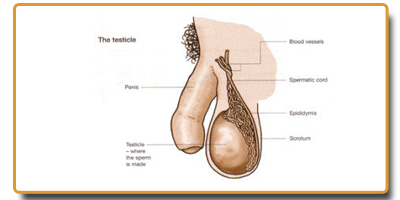
Collection of fluid around the testis in a sac is hydrocele. This can be assessed by clinical examination and confirmed by Ultrasound scan. Treatment is surgical which could be done as a day case.
Spermatocele:
Cyst with spermatic fluid found in the scrotum is spermatocele. They can form after vasectomy or occur without any known cause. These are removed if they cause symptoms through a small scrotal incision.
Testicular infection:
This is caused by bacterial or viral infection affecting either epididymis or testis or both. This is associated with pain and swelling of the testis and scrotum with or without fever. It needs be treated with pain killers, anti-inflammatory as well as antibiotics if necessary. In children and young adults one needs to differentiate it from acute torsion of testis and hence an urgent consultation with doctors is needed.
Testicular torsion:
In this condition the testicle twists and stays twisted in the scrotum rather than unwinding as one would expect. The twisting shuts off the blood supply to the testicle, which causes intense pain. The patient has sudden severe pain. This is a surgical emergency and needed immediate attention by a doctor and is treated by an operation.
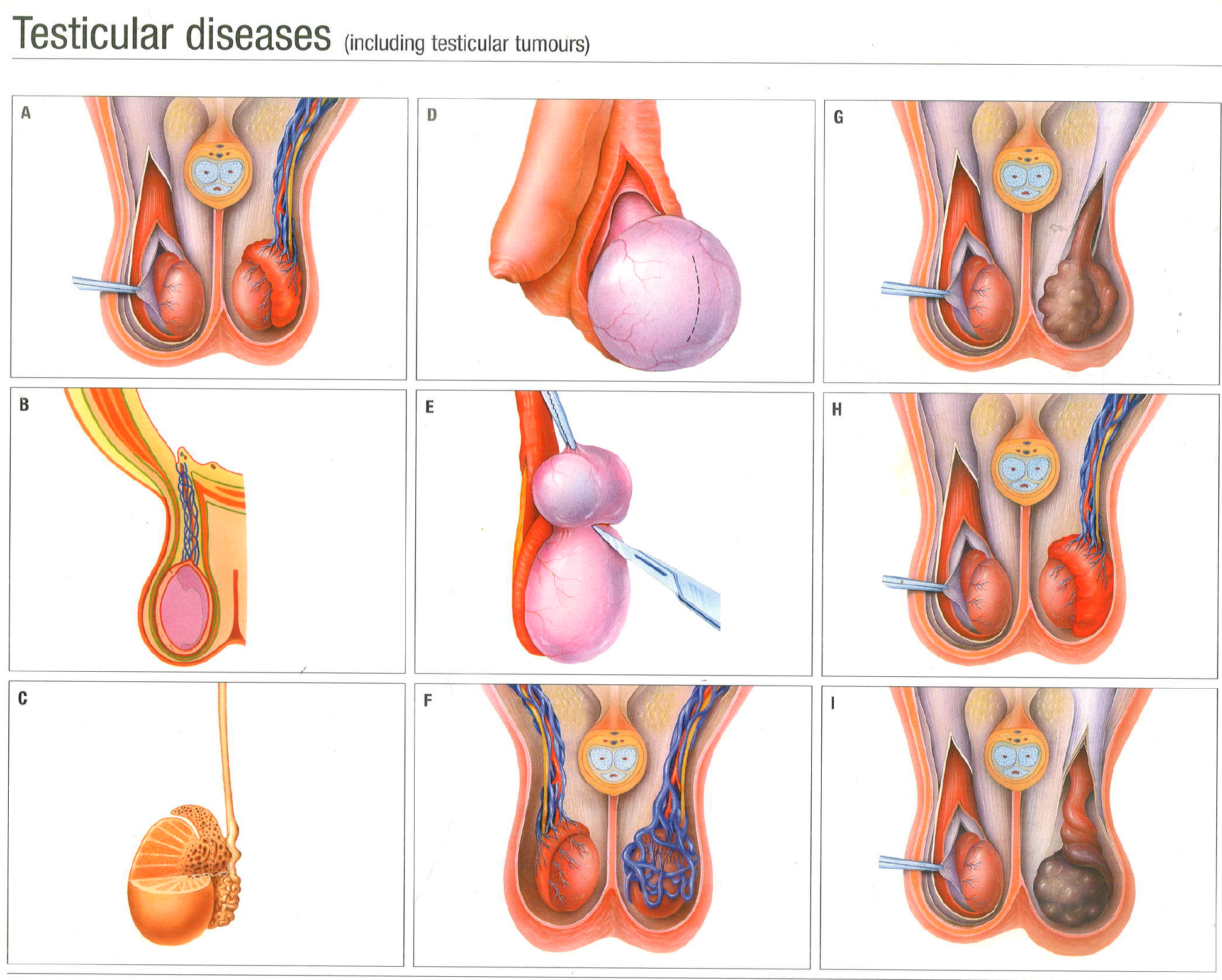
Testicular Cancer :
Onset of the painless swelling needs attention by a doctor as it could be a testicular cancer. It is diagnosed by a physical examination, ultrasound testis as well as blood tests. In the vast majority of patient, removing the testis through a Groin incision is required. Further treatments with chemotherapy or surgery may also be required.
Chronic scrotal pain:
A variety of conditions are responsible for this condition. This includes infective as well as non infective causes. It affects the quality of life of the patients and treatments are long and only partly successful. A consultation with a specialist is required.